Page 93 - Vol.03
P. 93
Special Report 特別企劃 Tech Notes 技術專文 New Visions 新象新知 LOHAS Column 樂活園地
090 091
Using ‘TransMembrane conventional treatment processes such PROCESS through the porous wall due to surface
ChemiSorption’ (TMCS) for as extraction, stripping or absorption DESCRIPTION tension effect. Because of the very low
can lead to several problems or issues.
Henry constant and high solubility
Ammonia Removal from Industrial For example, a stripping column has a mmonium ion (NH4+) in of NH3 compared to other dissolved
gases in water (e.g., CO2 or O2), the
relatively large footprint and is energy
water reacts with hydroxide
intensive due to complete pressure
free ammonia gas will be difficult to
Waste Waters loss of the treated water. In addition, Aion (OH-) according to the remove by applying vacuum or sweep
following Equation 1.
gas-vacuum combination as in typical
a secondary striping unit is needed to
clean up the striping media air before NH + OH ↔ NH 3 (g ) + H 2 O (l ) Eq 1 degassing operations with Membrane
+
−
4
以中空絲膜取出廢水中的氨氮 the air is vented to the atmosphere. This reaction is reversible and can be Contactor technology [2]. However, an
acid solution will work very effectively
Such issues may be overcome by using
an alternate solution called Membrane driven forward or backward depending as a means of removing the ammonia
3
3
1
1
1
文│Stasiak Ulbricht Schneid Munos² Sengupta² Kitteringham² Wiesler² 李玫 王義信 │ Contactor technology. Membrane gas from waste water. The low-pH
1 2 3 on the water pH as shown in Figure 1.
Membrana GmbH Membrana Charlotte 新廠設計部│ Contactors can remove ammonia from sulphuric acid solution will instantly
waste water and recover it to a usable react with ammonia gas according to
The extraction of ammonia using membrane contactors provides several advantages in solving a common problem in the form in a single step. It is therefore an Fig.1. Solubility of Free Ammonai Equation 2 below to form ammonium
Based on pH and Temperature
wastewater streams of many industries. Some possibilities and limitations of the ammonia removal process will be shown adequate and desirable solution for sulphate. This will generate and
based on experience gained through pilot studies. These pilot systems provide data that will allow scale up to full-sized treating the ammonia waste water maintain the concentration differential
commercial plants under comparable without polluting the air. or driving force for removing ammonia
conditions. R e mo va l o f a m mon i a u s i n g from waste water.
With this separation technique, hydrophobic hollow fiber membranes NH 3 /NH 4
ammonia as a gas species is stripped in Membrane Contactors has been 2NH + H 2 SO ↔ (NH 4 ) SO 4 Eq 2
3
4
2
from an aqueous liquid “feed” phase tested on small pilot systems in the
and captured into an aqueous liquid past. There is currently very limited The process above generates a
“receiving” phase in the same membrane data available on large scale field concentrated solution (up to 30%)
device. The membrane used in this installations. Because there is limited pH of ammonia sulphate, which is a
process is a microporous hydrophobic data there is insufficient knowledge fertilizer. This process, also described
hollow fiber, with no inherent selectivity about how to design and size full scale At a pH of 11.3 or higher, the as: “TransMembraneChemiSorbtion”
between permeating species. Because systems. Operating parameters such as equilibrium favors the formation of free (TMCS) [3], is shown schematically
the membrane is hydrophobic it can be waste water flow rate, pH, temperature, ammonia gas which can be removed on a commercial available hollow fiber
used to separate the feed phase and the and the ammonia concentration will from a waste water solution across Membrane Contactor Modul as well
receiving phase; the membrane pores are significantly impact the ammonia the air filled pores of a microporous as on a single fiber in Figure 2. The
essentially gas-fi lled. removal characteristics and removal hydrophobic membrane when a proper wastewater flows through shellside of
This paper presents data from pilot trials
and a full size plant where commercial
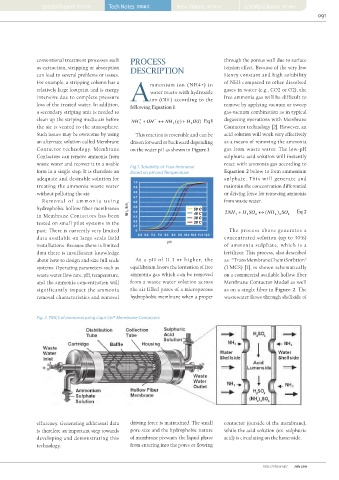
membrane contactors are used to remove Fig. 2. TMCS of ammonia using Liqui-Cel® Membrane Contactors
and recover ammonia from a wastewater
stream at an industrial site. Actual
waste water from the site containing
high concentrations of ammonia was
introduced on the shell side and a dilute
sulphuric acid solution was introduced
on the lumen side of the hollow fibers
inside of the modules. Prior to entering the membrane system the wastewater was dosed with a sodium hydroxide solution
to raise the pH. Raising the pH increases the partial pressure of free ammonia in the wastewater making it possible to
remove. The gaseous NH3 diffuses from the waste water phase across the micro porous hollow fi ber membrane wall and
reacts with sulphuric acid in the strip solution to form ammonium sulphate.
INTRODUCTION treatment plants. This translates into high penalty fees that
are paid by the company discharging these contaminates efficiency. Generating additional data driving force is maintained. The small contactor (outside of the membrane),
issolved gases like NH3, H2S or NOx in waste into the sewage stream. In many cases a membrane- is therefore an important step towards pore size and the hydrophobic nature while the acid solution (ex. sulphuric
water lead to contamination in the sewage system based water treatment system can be justified because of developing and demonstrating this of membrane prevents the liquid phase acid) is circulating on the lumenside.
Dand high treatment costs for municipal waste water a favorable pay back time. Large-scale processing using technology. from entering into the pores or flowing
NEW FAB TECHNOLOGY JOURNAL http://nfjournal/ July 2011