Page 50 - Vol.06
P. 50
Tech
Notes
技術專文
3.0
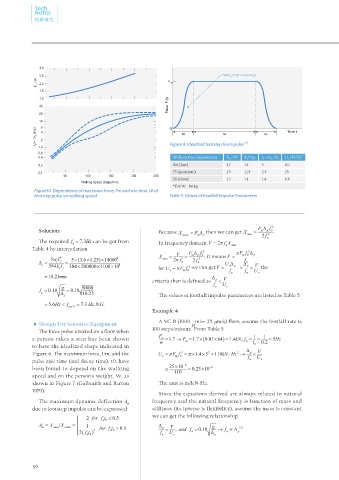
2.5 F(t)/F m =1/2[1-cos(πt/t 0 )]
F m /W 2.0 F m
1.5
1.0
40 Force F (t)
20
10 6 O
f o /= 1/t o (Hz) 4 2 to to to Time t
1.0 Figure 9. Idealized footstep force pulse [2]
0.6
0.4 Walking Pace steps/minute F m / W F m * kg f 0 = 1/t 0 , Hz U v kN-Hz 2
0.2 100 (fast) 1.7 1.4 5 110
0.1 75 (moderate) 1.5 1.25 2.5 25
50 100 150 200 250
50 (slow) 1.3 1.1 1.4 6.8
Walking Speed (Steps/min)
*For W = 84 kg
Figure10. Dependence of maximum force, Fm and rise time, t0 of
footstep pulse on walking speed Table 5. Values of Footfall Impulse Parameters
Solution: Because then we can get
The required can be got from In frequency domain:
Table 4 by interpolation
, it means
we can get the
criteria then is defined as
The values of footfall impulse parameters are listed as Table 5.
Example 4
• Design For Sensitive Equipment A VC-B (1000 in/s= 25 m/s) floor, assume the footfall rate is
The force pulse exerted on a floor when 100 steps/minute. From Table 5
a person takes a step has been shown
to have the idealized shape indicated in
Figure 6. The maximum force, Fm, and the
pulse rise time (and decay time), t0, have
been found to depend on the walking
speed and on the person's weight, W, as
shown in Figure 7 (Galbraith and Barton The unit is m/kN-Hz.
1970).
Since the equations derived are always related to natural
The maximum dynamic deflection frequency and the natural frequency is function of mass and
due to footstep impulse can be expressed: stiffness (its inverse is flexibility), assume the mass is constant
we can get the following relationship
50