Page 9 - Vol.17
P. 9
future laboratory functionality is
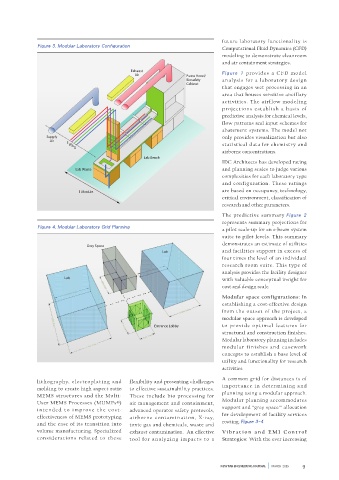
Figure 3. Modular Laboratory Configuration
Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD)
modeling to demonstrate cleanroom
and air containment strategies.
Exhaust
Air Fume Hood/ Figure 1 prov ides a CFD model
Biosafety analysis for a laboratory design
Cabinet
that engages wet processing in an
area that houses sensitive ancillary
activities. The airflow modeling
projections establish a basis of
predictive analysis for chemical levels,
flow patterns and input schemes for
abatement systems. The model not
Supply only provides visualization but also
Air E W A statistical data for chemistry and
G
airborne concentrations.
Lab Bench
IDC Architects has developed rating
Lab Waste and planning scales to judge various
complexities for each laboratory type
and configuration. These ratings
1 Module are based on occupancy, technology,
critical environment, classification of
research and other parameters.
The predictive summary Figure 2
represents summary projections for
Figure 4. Modular Laboratory Grid Planning
a pilot scale-up for an e-beam system
suite to pilot levels. This summary
demonstrates an estimate of utilities
Grey Space
approaches include: Lab and facilities support in excess of
- Photo-lithography techniques four times the level of an individual
- E-beam lithography techniques research room suite. This type of
- Ion-Beam lithography techniques analysis provides the facility designer
Lab with valuable conceptual insight for
- Nano-imprint lithography
- Nanofabrication by self-assembly cost and design scale.
- Laser technology processes Modular space configurations: In
Each and al l of these advanced establishing a cost-effective design
processes have various critica l from the outset of the project, a
env i r o n men t i s s u es a f fe c t i n g modular space approach is developed
Entrance Lobby to provide optimal features for
structural and construction finishes.
Modular laboratory planning includes
modular finishes and casework
concepts to establish a base level of
utility and functionality for research
activities.
A common grid for distances is of
lithography, electroplating and flexibility and presenting challenges
importance in determining and
molding to create high aspect ratio to effective sustainability practices.
MEMS structures and the Multi- These include bio processing for planning using a modular approach.
User MEMS Processes (MUMPs®) air management and containment, Modular planning accommodates
i nte nd ed to i mprove t he cost- advanced operator safety protocols, support and “grey space’” allocation
effectiveness of MEMS prototyping airborne contamination, X-ray, for development of facility services
and the ease of its transition into toxic gas and chemicals, waste and routing. Figure 3~4
volume manufacturing. Specialized exhaust contamination. An effective V ib r a t ion a n d E M I C on t r o l
considerations related to these tool for analyzing impacts to a Strategies: With the ever increasing
NEW FAB ENGINEERING JOURNAL MARCH 2015 9