Page 13 - Vol.10
P. 13
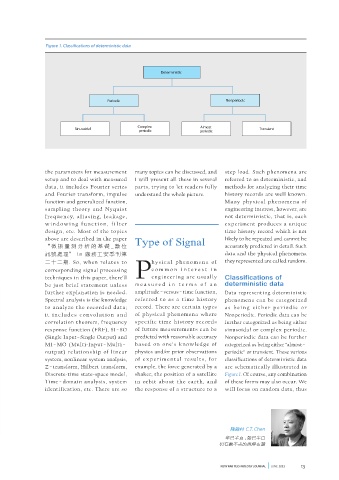
Figure 1. Classifications of deterministic data
Deterministic
& Spectral Periodic Nonperiodic
Complex Almost
Sinusoidal periodic periodic Transient
the parameters for measurement many topics can be discussed, and step load. Such phenomena are
setup and to deal with measured I will present all these in several referred to as deterministic, and
data, it includes Fourier series parts, trying to let readers fully methods for analyzing their time
and Fourier transform, impulse understand the whole picture. history records are well known.
function and generalized function, Many physical phenomena of
sampling theory and Nyquist engineering interest, however, are
frequency, a l iasing, leakage, not deterministic, that is, each
w i nd ow i n g f u nct ion , f i lt e r experiment produces a unique
design, etc. Most of the topics time history record which is not
above are described in the paper Type of Signal likely to be repeated and cannot be
“ 微振量測分析的基礎_數位 accurately predicted in detail. Such
訊號處理” in 廠務工安季刊第 data and the physical phenomena
二十二期. So, when relates to hy s ic a l phenomen a o f they represented are called random.
corresponding signal processing c o m mon i n t e r e s t i n
techniques in this paper, there’ll Pengineering are usually Classifications of
be just brief statement unless m e a s u r e d i n t e r m s o f a n deterministic data
further explanation is needed. amplitude– versus– time function, Data representing deterministic
Spectral analysis is the knowledge referred to as a time histor y phenomena can be categorized
to analyze the recorded data; record. There are certain types a s b e i n g e i t h e r p e r i o d i c o r
it i nc lud e s convolut ion a nd of physical phenomena where Nonperiodic. Periodic data can be
correlation theorem, frequency specific time history records further categorized as being either
response function (FRF), SI –SO of future measurements can be sinusoidal or complex periodic.
(Single Input – Single Output) and predicted with reasonable accuracy Nonperiodic data can be further
MI–MO (Multi-Input –Multi– based on one’s knowledge of categorized as being either “almost –
output) relationship of linear physics and/or prior observations periodic” or transient. These various
system, nonlinear system analysis, of e x per i menta l resu lts, for classifications of deterministic data
Z –transform, Hilbert transform, example, the force generated by a are schematically illustrated in
Discrete-time state-space model, shaker, the position of a satellite Figure 1. Of course, any combination
Time–domain analysis, system in orbit about the earth, and of these forms may also occur. We
identification, etc. There are so the response of a structure to a will focus on random data, thus
陳錦村 C.T. Chen
年已半百 , 髮已半白
仍有數不盡的挑燈夜讀
NEW FAB TECHNOLOGY JOURNAL JUNE 2013 13