Page 14 - Vol.10
P. 14
Tech
Notes
技術專文
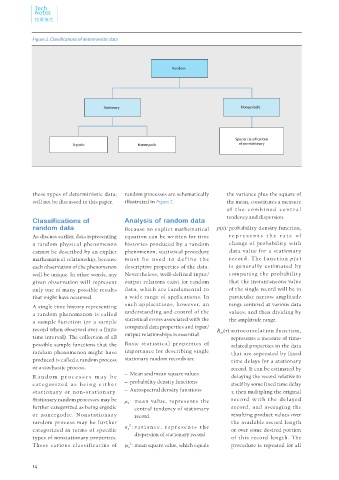
Figure 2. Classifications of deterministic data
Random
Stationary Nonperiodic
Special classi cations
Ergodic Nonergodic of nonstationary
these types of deterministic data; random processes are schematically the variance plus the square of
will not be discussed in this paper. illustrated in Figure 2. the mean, constitutes a measure
of t h e c o m b i n e d c e n t r a l
Classifications of Analysis of random data tendency and dispersion.
random data Because no explict mathematical p(x): probability density function,
As discuss earlier, data representing equation can be written for time r e p r e s e n t s t h e r a t e o f
a random physical phenomenon histories produced by a random change of probability with
cannot be described by an explict phenomenon, statistical procedure data value for a stationary
mathematical relationship, because m u s t b e u s e d t o d e f i n e t h e record. The function p(x)
each observation of the phenomenon descriptive properties of the data. is general ly estimated by
will be unique. In other words, any Nevertheless, well-defined input/ computing the probability
given observation will represent output relations exist for random that the instantaneous value
only one of many possible results data, which are fundamental to of the single record will be in
that might have occurred. a wide range of applications. In particular narrow amplitude
A single time history representing such applications, however, an range centered at various data
a random phenomenon is called understanding and control of the values, and then dividing by
a sample function (or a sample statistical errors associated with the the amplitude range.
computed data properties and input/
record when observed over a finite R xx (τ): autocorrelation function,
time interval). The collection of all output relationships is essential. represents a measure of time-
possible sample functions that the Basic statistical properties of related properties in the data
random phenomenon might have importance for describing single that are seperated by fixed
produced is called a random process stationary random records are time delays for a atationary
or a stochastic process. record. It can be estimated by
– Mean and mean square values
R a n d o m p r o c e s s e s m a y b e delaying the record relative to
c a t e gor i z e d a s b e i n g e i t h e r – probability density functions itself by some fixed time delay
stationar y or non-stationar y. – Autospectral density funstions τ, then multipling the original
Stationary random processes may be μ x : mean value, represents the record w ith the delayed
further categorized as being ergodic central tendency of stationary record, and averaging the
or nonergodic. Nonstationar y record resulting product values over
random process may be further 2 the available record length
categorized in terms of specific σ x : v a r i a n c e , re p re s e n t s t h e or over some desired portion
types of nonstationary properties. dispersion of stationary record of this record length. The
2
These various classificatins of ψ x : mean square value, which equals procedure is repeated for all
14