Page 20 - Vol.06
P. 20
Special
Report
特別企劃
Plant B 7.1
111.9
30.0 30.0
W 6
5.7 22.9
R 33.0 33.3
C 0.3 7 R
W 2.4
0.3 53.3
55.0 28.3
8
54.7 25.0 6.7 35.0
5.6 9 11
25.0
196.8 R 23.2
70.0 40.0
W 10 75.6 C 16.8 12
W
5.3
Plant A 3.5 45.0 15 20.9 13 8.0
24.1 2.7
50.0
1
16.4
49.9 49.9
33.6 2 34.0 14
113.1 R 30.5
8.0 8.0 Plant C R
W 4 C
W
51.6 3.2 7.9 7.9
5 R
0.1
3
54.8
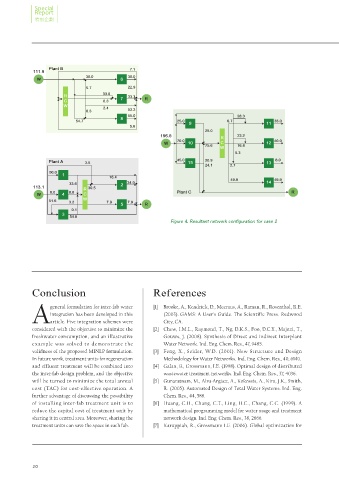
Figure 4. Resultant network configuration for case 2
Conclusion References
A [1] Brooke, A., Kendrick, D., Meeraus, A., Raman, R., Rosenthal, R.E.
general formulation for inter-fab water
(2003). GAMS: A User's Guide. The Scientific Press. Redwood
integration has been developed in this
City, CA.
article. Five integration schemes were
considered with the objective to minimize the [2] Chew, I.M.L., Raymond, T., Ng, D.K.S., Foo, D.C.Y., Majozi, T.,
freshwater consumption, and an illustrative Gouws, J. (2008). Synthesis of Direct and Indirect Interplant
example was solved to demonstrate the Water Network. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 47, 9485.
validness of the proposed MINLP formulation. [3] Feng, X., Seider, W.D. (2001). New Structure and Design
In future work, treatment units for regeneration Methodology for Water Networks. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 40, 6140.
and effluent treatment will be combined into [4] Galan, B., Grossmann, I.E. (1998). Optimal design of distributed
the inter-fab design problem, and the objective wastewater treatment networks. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 37, 4036.
will be turned to minimize the total annual [5] Gunaratnam, M., Alva-Argáez, A., Kokossis, A., Kim, J.K., Smith,
cost (TAC) for cost-effective operation. A R. (2005). Automated Design of Total Water Systems. Ind. Eng.
further advantage of discussing the possibility Chem. Res., 44, 588.
of installing inter-fab treatment unit is to [6] Huang, C.H., Chang, C.T., Ling, H.C., Chang, C.C. (1999). A
reduce the capital cost of treatment unit by mathematical programming model for water usage and treatment
sharing it in central area. Moreover, sharing the network design. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 38, 2666.
treatment units can save the space in each fab. [7] Karuppiah, R., Grossmann I.E. (2006). Global optimization for
20