摘要

專案管理系統發展之研究與討論
系統工具結合方法與理論,在專案管理中扮演著日益重要的角色。適當的系統工具將會是專案成功有利的助手,衡量的依據,更是專案經驗傳承與複製的重要媒介。如何利用現有的系統工具與開發新的系統功能,一直是組織持續在進行的重要課題。本文即希望透過方法理論檢視、內部意見蒐集與外部系統的比較,了解目前內部專案管理系統(Professional construction management system-PCM)的定位與優缺點,以作為未來持續強化管理方法與系統應用之參考。
前言
依據專案管理知識體系(PMBOK)所言,專案管理是將各種知識、技能、工具和技術應用於專案活動中,以達到專案需求。而專案管理專家Harold Kerznern所著的專案管理一書提到專案管理是針對相對短期的目標去規劃、組織、指導與控制公司的資源。並利用系統化的方法將垂直體系職能分工的人員安排至水平體系專案中。因此,論及專案管理,除了知識理論外,工具與方法也是相當重要的元素之一,而隨著專案類型日趨複雜與多元,專案管理資訊系統之發展也日益蓬勃。
近年來,新工處在團隊經驗持續累積與彙集下,也自行建立了一套專案管理系統(Professional construction management system-PCM)。希望透過理論的檢視與內外部資源檢討,勾勒目前系統發展定位與尋求未來可能的發展方向。
專案管理的發展與演進
在20世紀經營管理的演進史中,專案的時間管理與工作排程扮演著重要的角色。其中重要的里程碑包括:1917年曾與管理科學之父泰勒(Frederick W. Taylor)與亨利.甘特(Henry L. Gantt)共同提出的甘特圖工作分解結構(Work Breakdown Structure,WBS)與時間排程的管理技術;1930年代應用發展於紐約帝國大廈建造的流線排程法(Flow-line scheduling)。1940年代固特異輪胎(Goodyear)採用的里程碑圖(Milestone Charts)及排程平衡法(Line of Balance);1950發展的計畫評核法(Program Evaluation and Review Technique,PERT)與要徑法(CPM);1956年杜邦(DuPont)的詹姆斯.凱力(James Kelly)與摩根.渥克(MorganWalker)發展之箭頭活動排程(Activity-on-Arrow,AOA)。
在1960年代末,美俄冷戰達到高峰,計畫評核術(Program Evaluation and Review Technique,PERT)成為美國海軍大型武器系統發展的重要管理工具,並且衍生出「實獲值」(Earned Value Management,EVM)的大型專案合約管理工具,為當時許多政府機構採用。1969年PMI(Project Management Institute)成立,其後彙整專案管理理論,推出專案管理知識體系(PMBOK),將專案管理語言推行全球。而後隨著科技發展,製造業蓬勃發展,管理重心著眼至品質管理,流程再造與變革管理,具代表性的有1985年全面品質管理(Total Quality Management, TQM)、企業資源整合計畫(Enterprise Resource Planning,ERP)、豐田式及時庫存管理(Toyota Just in Time,JIT)、活動單元成本管理(Activity Based Costing /Management,ABC / M)、平衡計分卡(Balanced Scorecard,BSC)、六標準差流程專案管理、ISO9000認證等的發展。而後隨著組織的虛擬化,讓注重目標管理、生命周期成本(Life Cycle Cost)及人員調度彈性化的專案管理技術再度成為管理發展的重心。而後,隨著專案類型日趨龐雜,科技日新月異,如同王雪明教授在經理人雜誌發表之專案管理的趨勢與發展中所言,「為了增加專案流程的敏捷性與成本降低,許多大型研發專案利用鎖螺絲的螺旋漸進(Spiral Evolution)與技術介入(Technology Insertion)的概念,透過專案資訊系統(PMIS)整合全球供應商或合作夥伴,使專案發展的時間縮短,在市場主導性上(time to market)取得相對優勢。」利基於此緣由與近似背景,新工處的專案管理系統(Professional construction management system-PCM)也逐步建構而生。
圖一、專案管理綜述
 資料來源:Project Management, 2009, Harold kerznem
資料來源:Project Management, 2009, Harold kerznemPCM專案管理系統的發展
結合長期建廠累積的實務經驗,與專案管理知識體系(PMBOK)所定義的流程群組與知識領域(詳見 圖二),PCM在2003年建立了第一版發展雛型,透過網頁的呈現方式將資訊進行有條理的蒐集與發布。而後在新工處各部門團隊合作下,逐步加強各知識領域的控制流程,陸續開發了文件、時程、成本、安全、品質等管理模組。而為了再進一步強化各模組間的連結與安全控管,又在2011年與2012年進行程式整合,統合大部分系統之程式語言、控管模式與操作頁面,進而有了目前PCM系統的面貌。
圖二、PCM 網頁演變歷程

|
Knowledge Area\Process Groups |
Initiating |
Planning |
Executing |
Controlling |
Closing |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
4. Project IntegrationManagement |
5.1 Initiation |
4.1 Planning PlanDevelopment |
4.2 Project Plan Execution |
4.3 Integrated Change |
|
|
5. Project Scope Management |
|
5.2 Scope Planning 5.3 Scope Definition |
|
5.4 Scope Verification 5.5 Scope Change Control |
|
|
6. Project Time Management |
|
6.1 Activity Definition 6.2 Activity Sequencing 6.3 Activity DurationEstimating |
|
6.5 Schedule Control |
|
|
7. Project Cost Management |
|
7.1 Resource Planning 7.2 Cost Estimating 7.3 Cost Budgeting |
|
7.4 Cost Control |
|
|
8. Project Quality Management |
|
8.1 Quality Planning |
8.2 Quality Assurance |
8.3 Quality Control |
|
|
9. Project Human Resource Management |
|
9.1 OrganizationalPlanning 9.2 Staff Acquisition |
9.3 Team Development |
9.3 Team Development |
|
|
10. Project CommunicationsManagement |
|
10.1 CommunicationsPlanning |
10.2 Information Distribution |
10.2 Information Distribution |
10.4 Administrative Closure |
|
11. Risk Project Management |
|
11.1 Risk ManagementPlanning 11.3 Qualitative Risk Analysis 11.4 Quantitative Risk Analysis 11.5 Risk ResponsePlanning |
|
|
|
|
12. Project Procurement Management |
|
12.1 ProcurementPlanning 12.2 SolicitationPlanning |
12.3 Solicitation 12.4 Source Selection 12.5 Contract Administration |
|
12.6 Contract Closeout |
資料來源:A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge, 2000,Project Management Institute, Inc
而在改版系統逐步上線後,希望能夠近一步了解系統的優缺點,作為當下系統修訂的參考與未來發展藍圖的建構。因而在去年第三季,採用問卷法、深度訪談法、標竿法等三種方式,進行意見與資訊的收集。而透過問卷法與深度訪談法,總計蒐集25%組織人員的意見,主要的發現有:
- 85%受訪者同意PCM對提升工作效率確有助益;
- 71%受訪者同意PCM容易使用;
- 除了部份模組,超過50%不了解完整PCM的細部功能;
- 30%受訪者認為部分模組功能近似或重複。
而綜合受訪者意見可歸納出三個建議的改善方向:
- 須再加強使用者教育訓練與功能宣傳;
- 資料更新速度與正確性須再提升
- 須再強化使用者介面便利性。可作為後續PCM系統改善之參考。
外部系統標竿比較
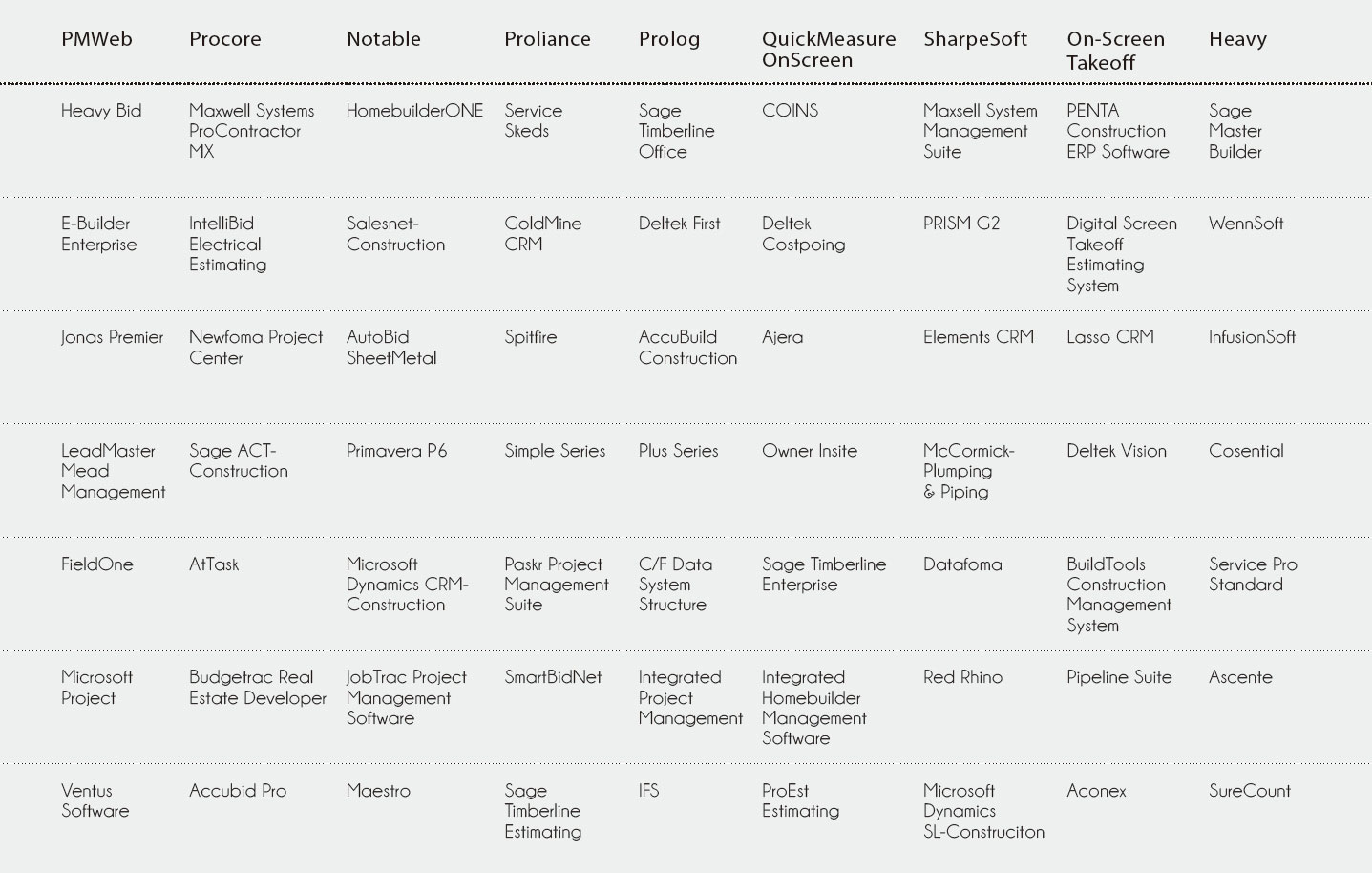
除了進行內部問卷調查與訪談外,同時也採用了標竿法進行外部資訊的收集與比較。初步透過網路搜尋,發現類似的系統全球超過數百家,因此先將搜尋範圍縮小至PMBOK的起源地─美國,找出72家廠商(如 圖三所示),大致搜尋其網頁後發現各家軟體設計架構大致相似,皆以九大知識領域與五大流程為系統主軸,因此再依客戶產業屬性與知名度挑選出三套系統:PMWeb、Procore、Notable進行細部功能比較。
圖三、網路現有專案管理系統調查 資料來源:本文整理
首先發現在主操作模組分類部份,這三個軟體和PCM有ㄧ個顯著差異為PCM是以知識領域為模組:分為專案範疇、時程管理、成本管理、品質管理、溝通管理、人力資源、風險與公安環保、採購管理八個領域。而此三個軟體之主操作界面是以工作操作界面為模組分類。以PMWeb為例,主操作模組分為:計畫、工程表單、成本管理、排程、資產管理、流程、時間表、文件管理、自定表單、整合管理等十大模組分類。這種定義方式接近直覺使用模式,應可加快使用者上手速度,或可做為PCM模組分類調整參考,或可考慮以雙矩陣方式加上此種操作選項於PCM系統。
再就細部功能做進一步比較分析,以組合管理(Portfolio Management )而言,PCM在此部份已有初步功能,惟指標與細部資料連結功能尚未完善,且尚未有跨專案之整合比較,以做為橫向專案管理之協助工具。而在採購管理方面,因公司已有採購其他採購平台,故PCM此部份僅提供連結供使用者連至既有採購平台,並未再新增功能。而在成本管理部份,外部三軟體約較PCM多了40~50%的功能,主要差異在外部三軟體多了趨勢分析、時間序列資訊比對、自動估算的工具,而PCM則較偏重報表的呈現(如 表二所示)。
|
Catogory |
PCM |
Software in the market |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Function |
Under same Platform |
Function |
Under same Platform |
|
|
Portfolio Management |
||||
|
General |
||||
|
Web based Platform with zero footprint |
Y |
Y |
Y |
|
|
Multi browser compatible (Google Chrome, IE, Safari) |
N |
Y |
Y |
|
|
Portfolio and cross-project management capability |
Y |
N |
Y |
Y |
|
Maps Integration with the ability to drill down to budget and schedule |
N |
Y |
Y |
|
|
Ability to drill down from portfolio to the program to the project all the way down to the document and the ability to roll back up from the document to the portfolio. |
N |
Y |
Y |
|
|
Purcurement Management |
||||
|
Procurement / Purchasing |
||||
|
Ability to link to Estimating |
N |
Y |
Y |
|
|
Import buyout items from Excel |
N |
Y |
Y |
|
|
Invitation to Bid |
N |
Y |
Y |
|
|
Online Bidding |
N |
Y |
Y |
|
|
Analyze bids in spreadsheet format |
Y |
N |
Y |
Y |
|
Create subcontract/purchase order from bid |
N |
Y |
Y |
|
|
Cost Management |
||||
|
Estimating |
||||
|
BIM Integration |
Y |
N |
Y |
Y |
|
Store item pricing in database |
Y |
N |
Y |
Y |
|
Advanced customizable formulas |
N |
Y |
Y |
|
|
Automatically create budget from estimates |
N |
Y |
Y |
|
|
Automatically create contracts from estimates |
N |
Y |
Y |
|
|
Estimate templates |
Y |
N |
Y |
Y |
|
Route estimates for approval |
Y |
N |
Y |
Y |
|
Budget |
||||
|
Unlimited budget code structure |
Y |
N |
Y |
Y |
|
User definable cost codes |
Y |
N |
Y |
Y |
|
Ability to use different cost codes across multiple projects |
Y |
N |
Y |
Y |
|
Ability to assign budget, contracts, and change orders to period |
Y |
N |
Y |
Y |
|
Ability to assign actual cost to periods |
Y |
N |
Y |
Y |
|
Trending Analysis |
N |
Y |
Y |
|
|
Previous period comparison |
N |
Y |
Y |
|
|
Historical Data Analysis |
N |
Y |
Y |
|
|
Funding |
||||
|
Separate funding codes |
Y |
N |
Y |
Y |
|
Funding requests |
Y |
N |
Y |
Y |
|
Funding authorization |
Y |
N |
Y |
Y |
|
Ability to assign contracts, change orders, and invoices to funding codes |
N |
Y |
Y |
|
|
Contracts |
||||
|
Ability to create prime/owner contracts |
Y |
N |
Y |
Y |
|
Ability to create subcontracts & purchase orders |
Y |
N |
Y |
Y |
|
Ability to add items to contract from library |
Y |
N |
Y |
Y |
|
Change Management |
||||
|
Change Events |
Y |
N |
Y |
Y |
|
Ability to add items to change event from library |
Y |
N |
Y |
Y |
|
Prime Contract Change Order |
N |
Y |
Y |
|
|
Subcontract Change Order |
N |
Y |
Y |
|
|
Billing |
||||
|
Link actual cost to requisition |
N |
N |
Y |
Y |
|
General Invoices |
N |
N |
Y |
Y |
|
Progress Invoices |
N |
N |
Y |
Y |
|
Update percent complete from schedule |
Y |
N |
Y |
Y |
而在文件管理部份,約有PCM約有40%功能與三軟體相似,主要差異為PCM在自定流程、自定表單、溝通紀錄、文件其他資源互相連結等方面功能選項較少,而PCM也較著重報表的呈現和不同文件間的流程差異。在時程管理上,排程管理、線性預測等時程管理元素是PCM與其他三軟體皆具備的基礎功能,惟PCM目前較少著墨於資源規劃、風險管理與結合時程的現金流推估。另在CCTV的管理工具上,目前PCM著重在及時現場的監控,基於隱私權的考量,尚未啟動及時錄影與拍照功能(如 表三所示)。
|
Catogory |
PCM |
Software in the market |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Function |
Under same Platform |
Function |
Under same Platform |
|
|
Document Management |
||||
|
Storage / Collaboration |
||||
|
Web-based central repository for the secure storage and publishing of documents |
Y |
N |
Y |
Y |
|
User defined attributes and metadata |
N |
Y |
Y |
|
|
Exchange documents across projects |
N |
Y |
Y |
|
|
Search bar that can search all details in forms |
Y |
N |
Y |
Y |
|
Document check-in and check-out |
N |
Y |
Y |
|
|
Link to CCTV |
N |
Y |
Y |
|
|
Link to Google Map |
N |
Y |
Y |
|
|
Link to any html Code |
N |
Y |
Y |
|
|
Link to any records in the database |
N |
Y |
Y |
|
|
Store photos/ films |
Y |
N |
Y |
Y |
|
Link to detailed document |
Y |
Y |
Y |
|
|
Construction Forms |
||||
|
Request for Information |
Y |
Y |
Y |
|
|
Meeting Minutes |
Y |
N |
Y |
Y |
|
Submittals |
Y |
N |
Y |
Y |
|
Conversation Log |
N |
Y |
Y |
|
|
Punch list |
Y |
Y |
Y |
Y |
|
Custom Form Builder |
||||
|
Ability to add user definable dates, lists, text, memo fields |
N |
Y |
Y |
|
|
Designate required fields |
Y |
Y |
Y |
Y |
|
User defined grids |
N |
Y |
Y |
|
|
Assign automated workflow to custom forms |
N |
Y |
Y |
|
|
Ability to assign custom forms by project |
N |
Y |
Y |
|
|
Workflow |
||||
|
Assign workflow users based on role |
Y |
Y |
Y |
|
|
Individual user "inbox" |
N |
Y |
Y |
|
|
Automated email notifications/alerts |
Y |
Y |
Y |
Y |
|
Displays notes to fully explain follow-up actions |
N |
Y |
Y |
|
|
Set due date by review time |
Y |
Y |
Y |
Y |
|
Ability to assign to proxy reviewer if user is unavailable (sick, vacation, etc...) |
N |
Y |
Y |
|
|
Ability to configure parallel workflow (anyone can approve, all can approve) |
Y |
Y |
Y |
Y |
|
Configure workflow process (add, edit, and remove steps), and provides an audit trail |
N |
Y |
Y |
|
|
Scheduling |
||||
|
General |
||||
|
Critical Path Method (CPM) |
Y |
N |
Y |
Y |
|
Enterprise and resource scheduling |
N |
Y |
Y |
|
|
Risk Management |
N |
Y |
Y |
|
|
Earned value |
Y |
N |
Y |
Y |
|
Automatic Linear Projection |
Y |
N |
Y |
Y |
|
Automatically distribute projection by curve, Front Loaded, Back Loaded, Bell Curve, etc… |
Y |
N |
Y |
Y |
|
Ability to compare actual to projected |
Y |
N |
Y |
Y |
|
Forecast multiple project Cashflow by region and fiscal year |
N |
Y |
Y |
|
|
CCTV |
||||
|
CCTV Management |
Y |
N |
Y |
Y |
|
Able to Store image or sections of film into document |
N |
Y |
Y |
|
在品質管理部份,尚無法就網頁確認其他三軟體的運作模式,故主要功能無從比較,惟發現市場現有軟體有設計及時資料自其他模組拖拉功能,而目前PCM各模組間較無此設計。
在報表部份,PCM較缺少整合報表,且在各層級報表與細項連結等部份功能也較缺乏。而專案整合指標平台─專案儀表板部份,PCM在近期改版時已加入此功能意向,惟在跨專案比較、使用者自定版型、不同角色之版型設計上目前功能上較少著墨。安全控管部份,PCM目前已導入新增安全控制統合中心,搭配原有程式之權限控制,已在功能上近似其他三軟體(如 表四所示)。
|
Catogory |
PCM |
Software in the market |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Function |
Under same Platform |
Function |
Under same Platform |
|
|
Quality and Safety Management |
||||
|
General |
||||
|
Ability to pull data from other functions |
Y |
N |
Y |
Y |
|
Link to detailed document within report |
Y |
N |
||
|
Reporting |
||||
|
Business Intelligence |
||||
|
Tracking earned value, resource usage, risk, cost, benefits or other criteria |
N |
Y |
Y |
|
|
Ability to drill down from multiple project to single project detail |
Y |
N |
Y |
Y |
|
Vendor's Daily/Weekly Report |
Y |
Y |
Y |
Y |
|
ESH's Daily/ Weekly Report |
Y |
Y |
Y |
Y |
|
Link to activties within report |
N |
Y |
Y |
|
|
Link to Vendors within report |
N |
Y |
Y |
|
|
Other documents can link to this report |
N |
Y |
Y |
|
|
BI Dashboards and Analytics |
||||
|
Role based dashboard |
N |
Y |
Y |
|
|
Subcontractor Navigator |
N |
Y |
Y |
|
|
Current financial trend analysis dashboard |
N |
Y |
Y |
|
|
Self Generate (Pie Chart, Bar Graph, S-Curve from database |
Y |
N |
Y |
Y |
|
Provides cross-project view |
N |
Y |
Y |
|
|
Provides executive view |
N |
Y |
Y |
|
|
Dynamic grouping |
N |
Y |
Y |
|
|
Dynamic HTML extensions for drill down to actual documents |
N |
Y |
Y |
|
|
Security |
||||
|
Role based or user based security |
Y |
N |
Y |
Y |
|
Security by project |
Y |
N |
Y |
Y |
|
Security by module |
Y |
N |
Y |
Y |
|
Security by form |
Y |
N |
Y |
Y |
|
Limit of Authority |
Y |
N |
Y |
Y |
|
Reporting Security |
N |
Y |
Y |
|
|
Professional Services / Administration |
||||
|
Implementation and Customization |
||||
|
Implement in less than sixty days |
N |
Y |
||
|
Deployment Options |
||||
|
Web based deployment (No citrix, or third party clients) |
Y |
Y |
Y |
|
|
ASP Model |
N |
Y |
||
|
Self-Hosted |
Y |
Y |
Y |
|
除個別功能比較外,尚發現因PCM各模組主要是先由水平各自發展而來,雖因權限控管、資料庫管理、操作紀錄管理等原因,在近一年已完成大部份程式改寫,但因尚有數個模組考慮程式撰寫資源分配與上線時程規劃考量,目前仍採個別程式開發並以平台和資料庫連結方式互通,因此PCM整體會較其他三軟體在平台系統一致性上略顯不齊。
結論
透過標竿法與外部系統就功能面逐一比較後,回頭檢視內部使用者之意見。發現除了個別系統操作與使用者界面人性化等問題須再持續改善外,另有兩個比較根本的專案管理問題更須同步搭配處理。ㄧ為工作分解結構(Work Breakdown Structure, WBS)、成本分解結構(Cost Breakdown Structure, CBS)與組織分解結構(Organizational Breakdown Structure, OBS) 等尚未建構完備。專案工作須經過系統整理分析,展開成分解結構之對應矩陣,使工作可以依照層級分類進行模組化管理及績效分析。在外部軟體設計中,皆可發現多以此分解結構做為系統基礎,而後再進行各種變化應用,因此各模組容易進行資料交換與統整,也可減少資料輸入之重工。這一部份目前已在PCM Schedule模組建立Project Appraisal Guide System-PAS進行工作分解結構之蒐集與整理,而近期也配合專案發包時程,重新檢討目前使用之成本分解結構,以期更符合專案現況與管理目標,同時須規劃發展輸入界面以系統化蒐集成本資料庫,以利未來與工作分解結構及組織分解結構矩陣對應成為PCM底層架構。
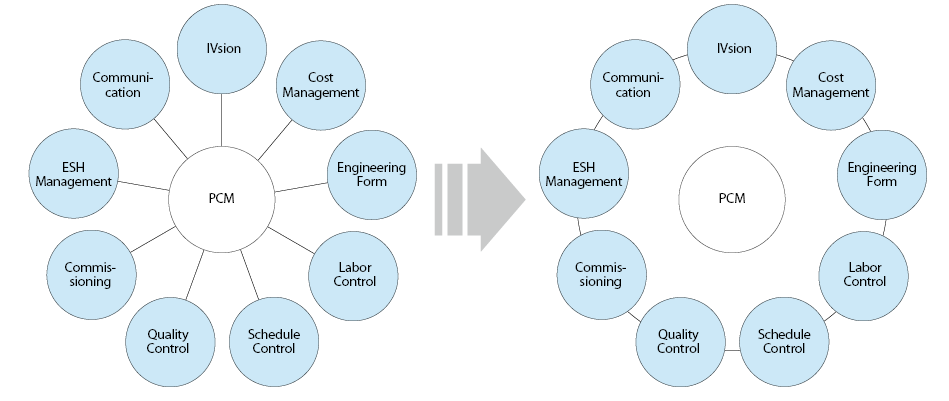
而其二則是須再針對PCM相關的工作流程進行定義,目前PCM各模組間相關性較弱,須透過定義工作流程,將各模組各自及相互的工作流程串接起來,才能使PCM確實成為專案工作者每日工作不可或缺之工具幫手。將PCM由平台概念強化為完整連結之系統(如 圖四所示)。
圖四、PCM 系統概念調整 資料來源:本文整理
參考文獻
- Project Management for Construction: Fundamental Concepts for Owners, Engineers, Architects and Builders (by Chris Hendrickson, Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Carnegie Mellon University, Pittsburgh)
- Project Management: A system s approach to planning, scheduling and control (by Harold kerzner, PH.D., The international institute for learning New York, 2009)
- Project and Cost Engineers’ Handbook Fourth Edition (by Kenneth K. Humphreys Ph.D., Consulting Engineer, Granite Falls, North Carolina, U.S.A.)
- A guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (Project Management Institute, Pennsylvania, U.S.A.)


留言(0)